Summary: In this Article, you’ll get to read about —
In today’s world, businesses have to deal with a large amount of data that comes from a variety of sources. They require a solution that is capable of handling and managing their data. Data warehouses were developed to facilitate the management of large amounts of data. A data warehouse is a specific kind of data management system that was developed to facilitate and assist operations associated with business intelligence, especially data analytics.
A cloud data warehouse is purely intended for query and analytical purposes, and they frequently store vast amounts of historical data gathered by organizations from many sources. These sources include a diverse selection of apps including log files and transaction programs among others. There are several tools such as RedShift.
What are Redshift and BigQuery?
Amazon’s Redshift database is a cloud data warehouse solution. Companies can store petabytes of data in easy-to-access “clusters” that can be searched in parallel using the platform’s storage system. Users and applications can access each of these nodes independently. Redshift is interoperable with a number of existing SQL-based clients and may be used with a range of data sources and data analytics tools.
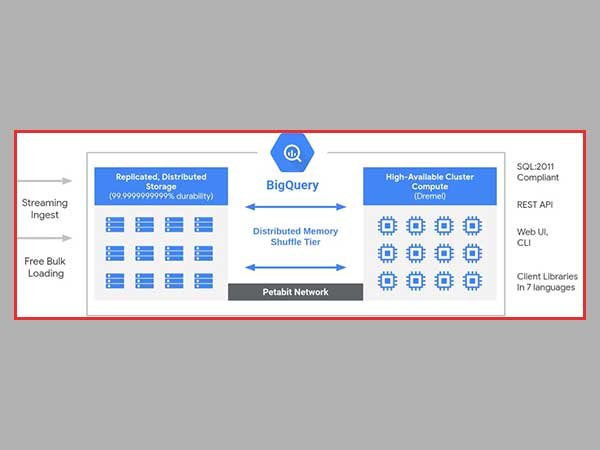
BigQuery is a fully managed enterprise data warehouse that comes with built-in technologies like machine learning, geospatial analysis, and business intelligence to help you manage and analyze your data. The serverless architecture of BigQuery allows you to use SQL queries to solve your organization’s most pressing problems while requiring no infrastructure management. BigQuery’s scalable and distributed analytical engine makes it possible to query terabytes of data in a matter of seconds and even petabytes of data in a matter of minutes.
Also, Read: The Role of Cloud Computing in the Internet of Things
Comparing RedShift and BigQuery
Both are used for data warehousing and provide different solutions to the organization. It usually depends upon the organization whether they want to deploy a proper data warehousing infrastructure or not. But let’s understand the basic key difference in both of them.
Architecture
When we talk about RedShift and Big Query, we should keep in mind that these two platforms often make use of fairly different architectures to deliver their various services. This is something that we should keep in mind when we talk about these things.
When we discuss the idea that underpins RedShift, we can state that it is analogous to that of infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) or platform-as-a-service (PaaS).
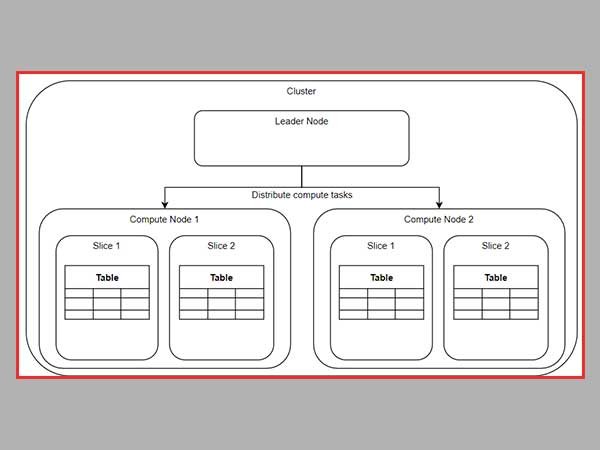
Customers are responsible for the provisioning of computing and storage nodes on the platform according to their preferences, and they are forced to take some amount of responsibility for capacity planning. It is extremely comparable to the process of managing and allocating all of the resources at your disposal.
When it comes to the approach that BigQuery takes, it is comparable to that of software-as-a-service (SaaS). Using BigQuery does not need any customers to deploy servers or rent storage space. Also, there is no need to worry about allocating resources or making any plans for the required amount of computational power. Thus, there is no need to worry about any of these things. You can acquire access to both the online user interface and the REST API by simply registering or creating an account on the relevant portal. This will enable you to instantly begin running queries against the relevant database.
Management
As Amazon Redshift is considered a self-managed system, it is the user’s responsibility to carry out all the system’s activities. These activities include the installation of hardware and software and the addition of computing and storage space. In addition to this, because storage and computation are not kept separate, it is important to set up the right clusters. In addition, the workflow for the data must be built keeping in mind the readily available resources. Maintenance in Amazon Redshift requires the user to periodically do tasks such as evaluating and removing the table for which a skilled professional is constantly required.
When we talk about Google BigQuery, we might consider it a serverless system as the majority of its activities are handled by Google on the Google Cloud Platform. Moreover, there is no need for sizing in the setup process because its storage nodes and compute nodes are kept separate and are handled by Google itself. So, users do not need proper managerial skills or professional training. All they need to get started is to create an account.
Scalability
Amazon Redshift is able to perform exceptionally well in terms of scaling. It can be used to scale concurrent files. It permits as many as 500 concurrent connections and as many as 50 concurrent queries to be run simultaneously in a cluster. As a result, it simultaneously processes several query requests. Additionally, it is able to scale both vertically and horizontally and provides several clusters with automatic access.
As BigQuery keeps its compute nodes and storage nodes separate and as these nodes are constantly handled by Google, it is up to the user to decide how to increase the amount of processing power and memory accessibility. This can be done with a few clicks. They are able to easily adjust the level of processing performed in accordance with the demands placed on them. This assists in the process of attaining great scalability of data (up to petabytes), which can be executed in real-time both vertically and horizontally.
Conclusion
BigQuery and Redshift are mostly used for processing data or data warehousing. These are very helpful for managing the data needs of the organization and forecasting future courses of action.
Both Redshift and BigQuery usually have their own benefits and organizations can compare these benefits to choose what suits them best. If the organization has someone professional who can manage everything then they can lean towards RedShift but if the organization wants a simple clean and clear interface without the hassling of managing the resources then they can go for the BigQuery.